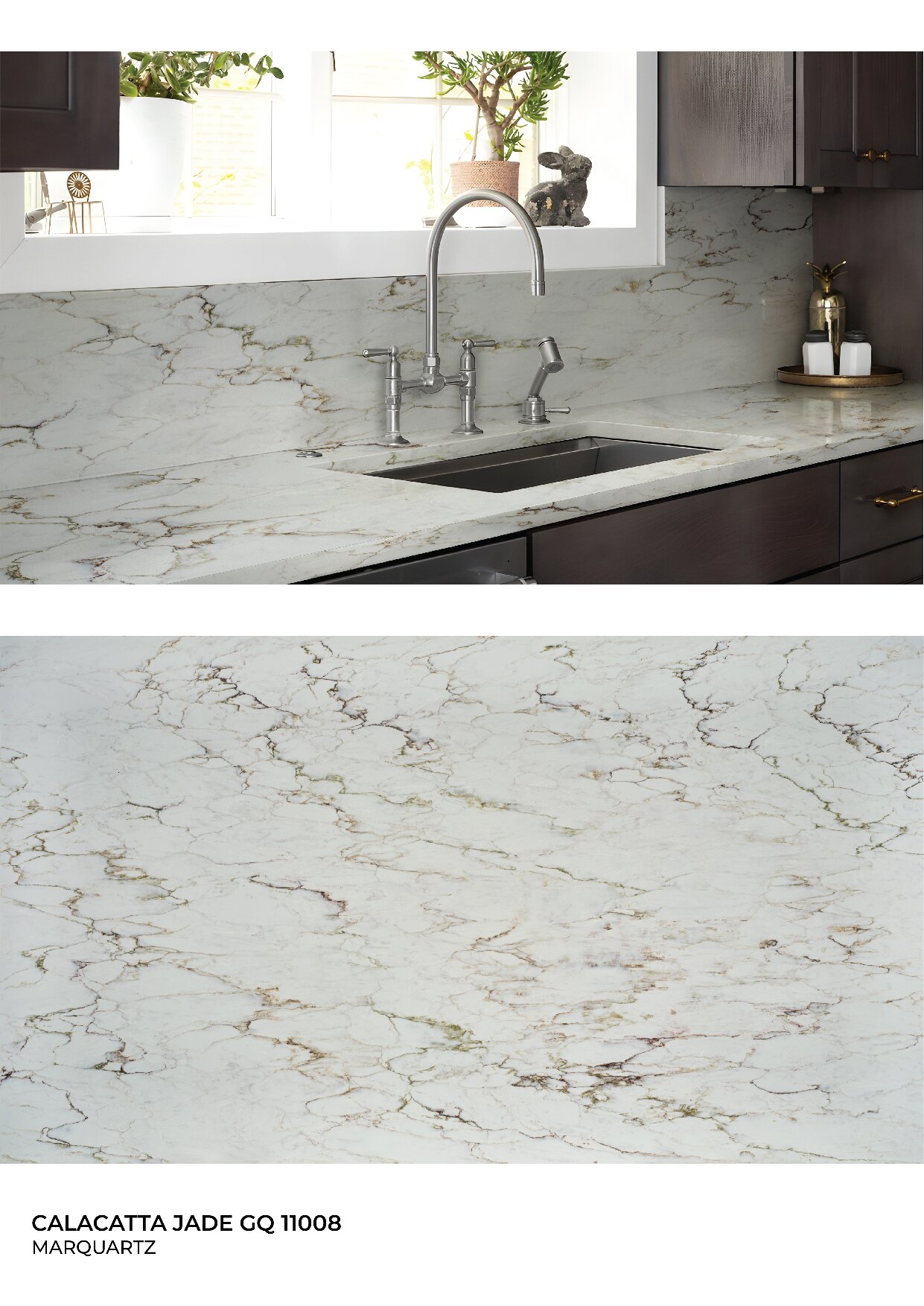
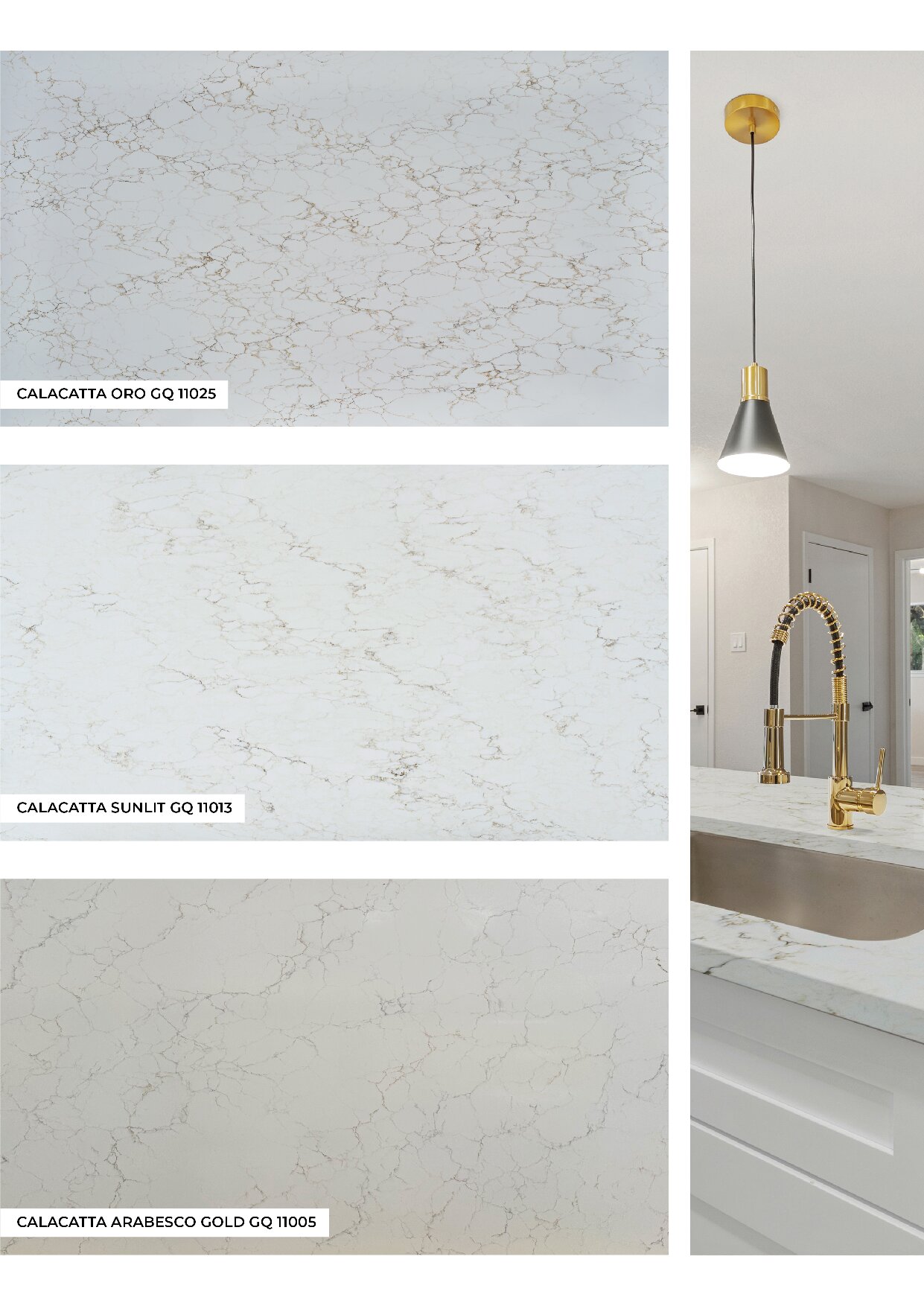
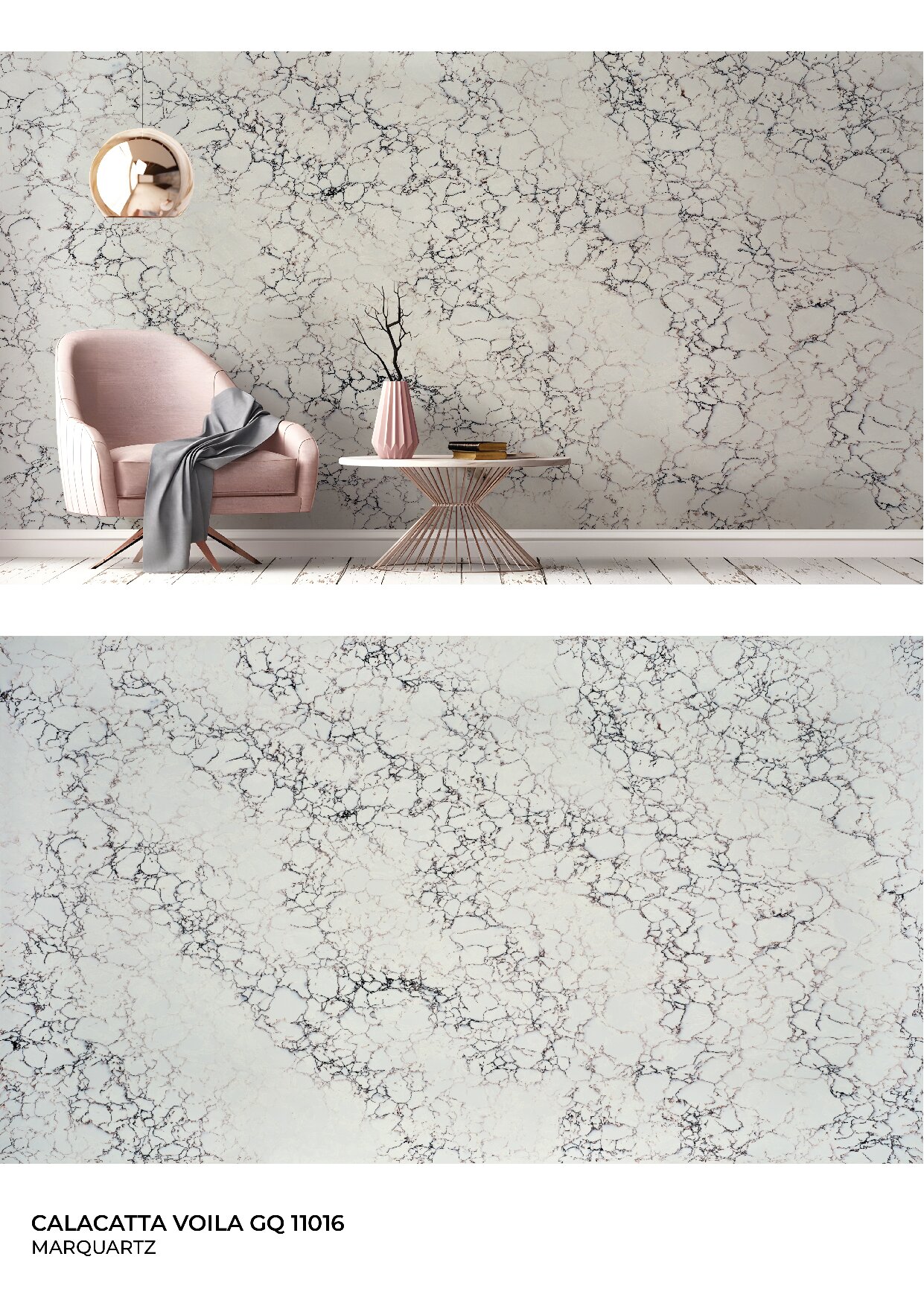
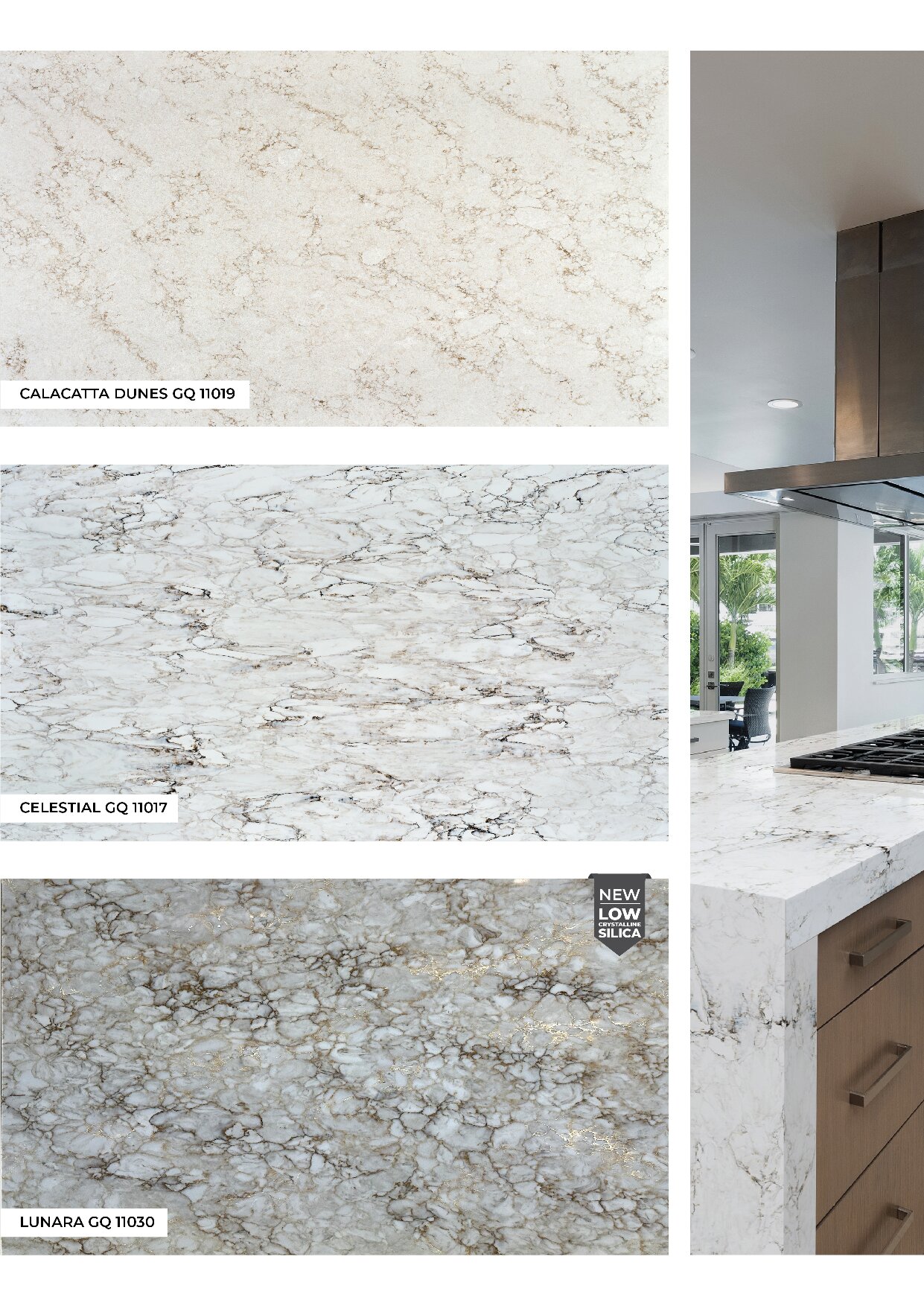
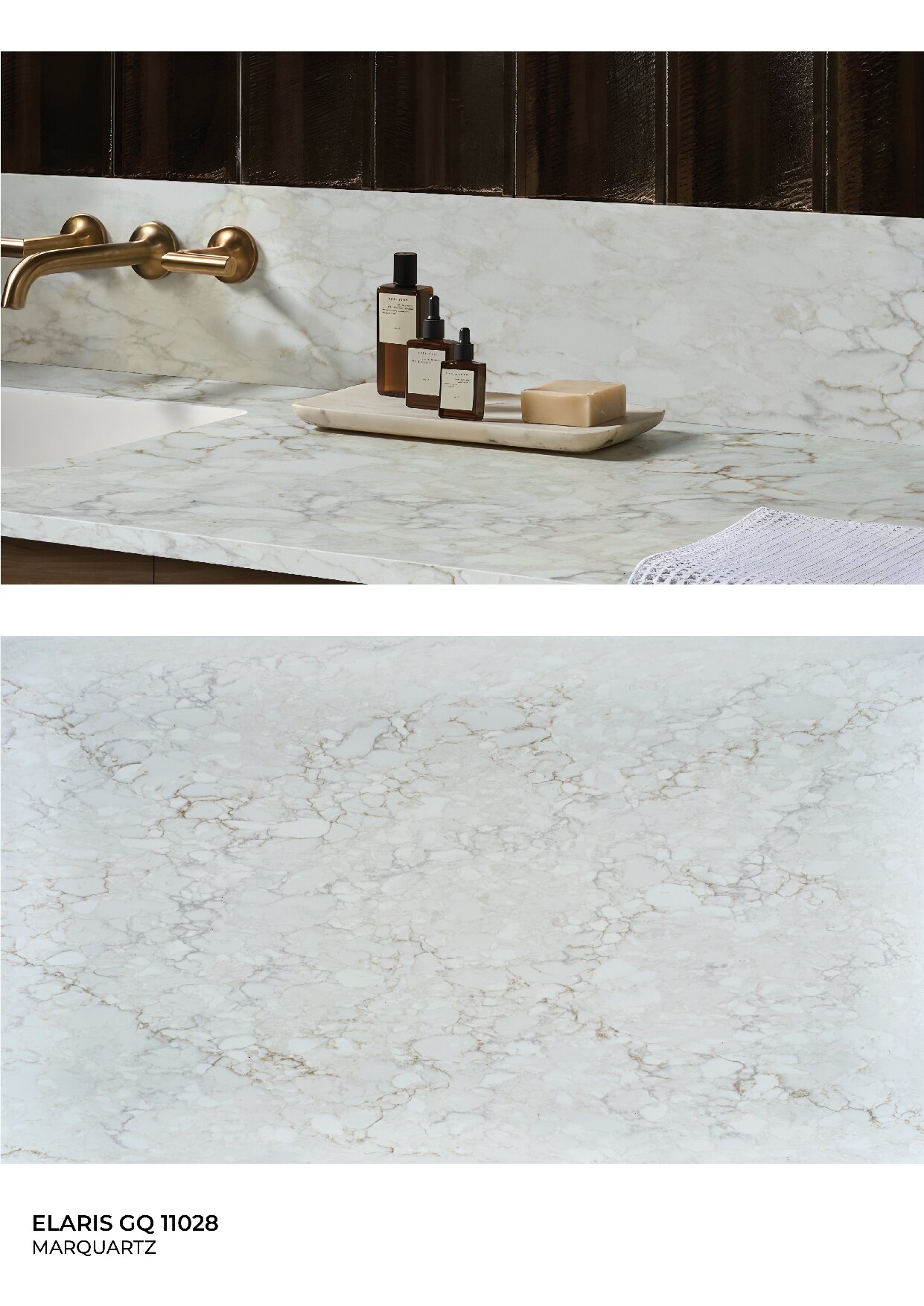
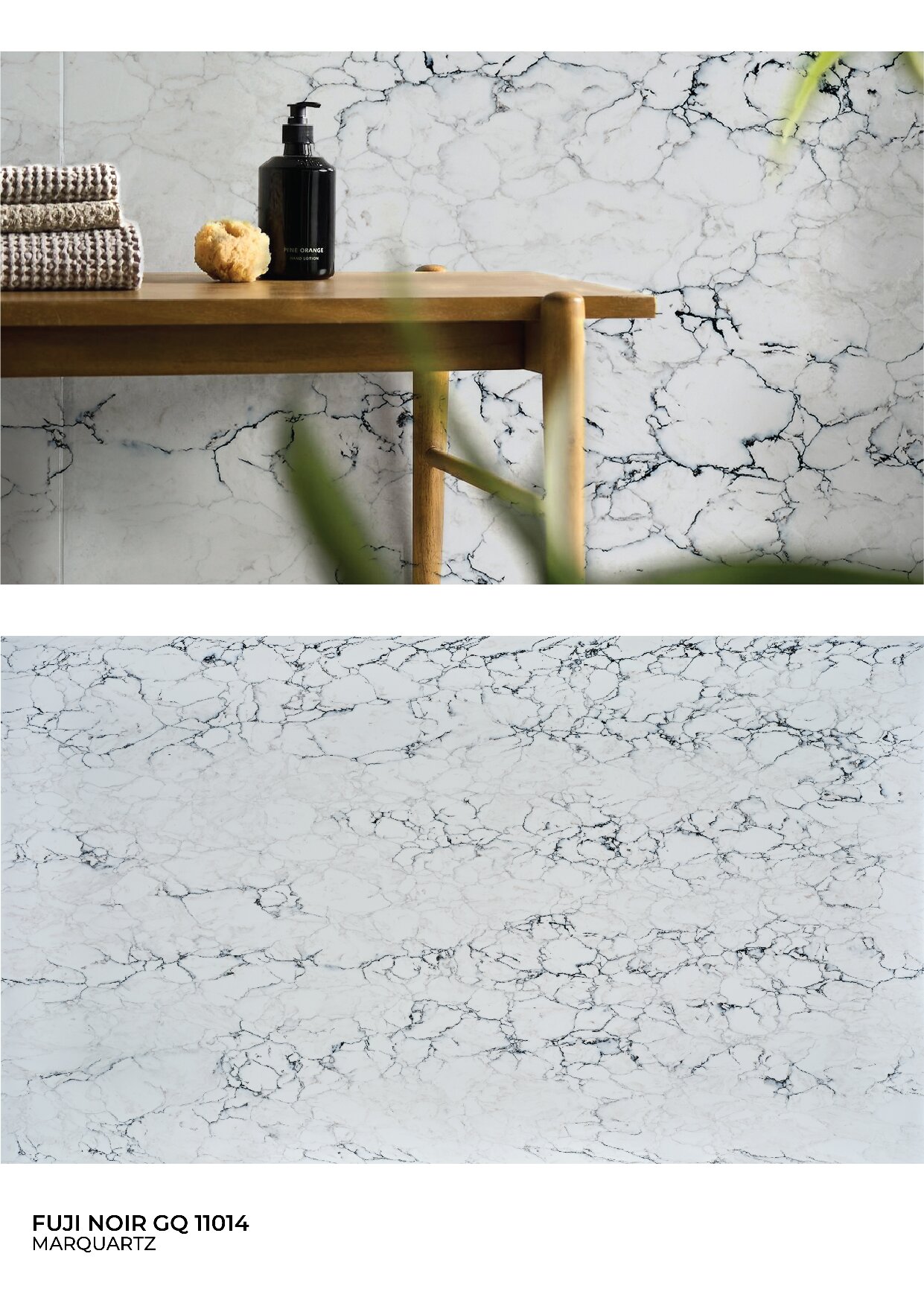
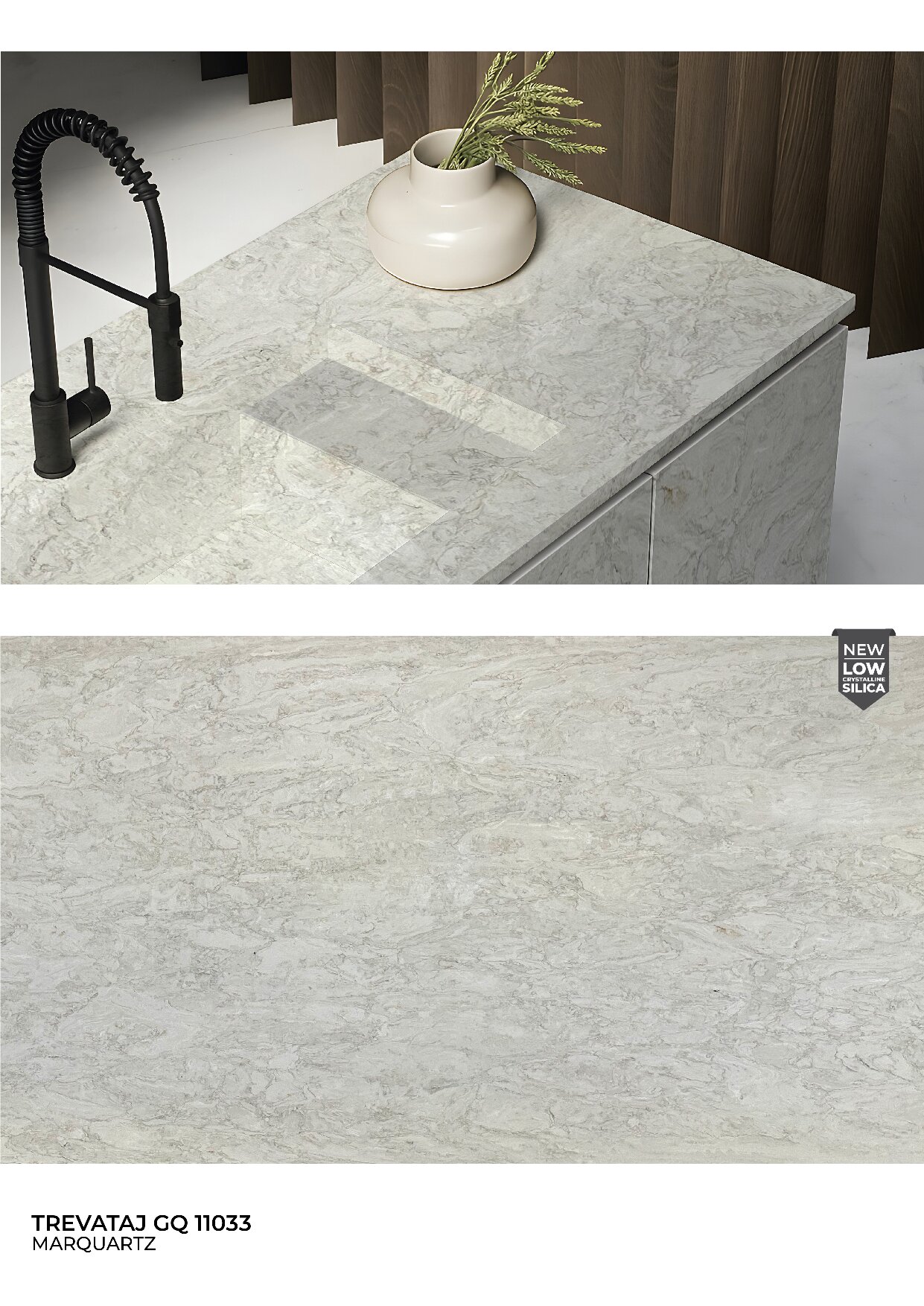
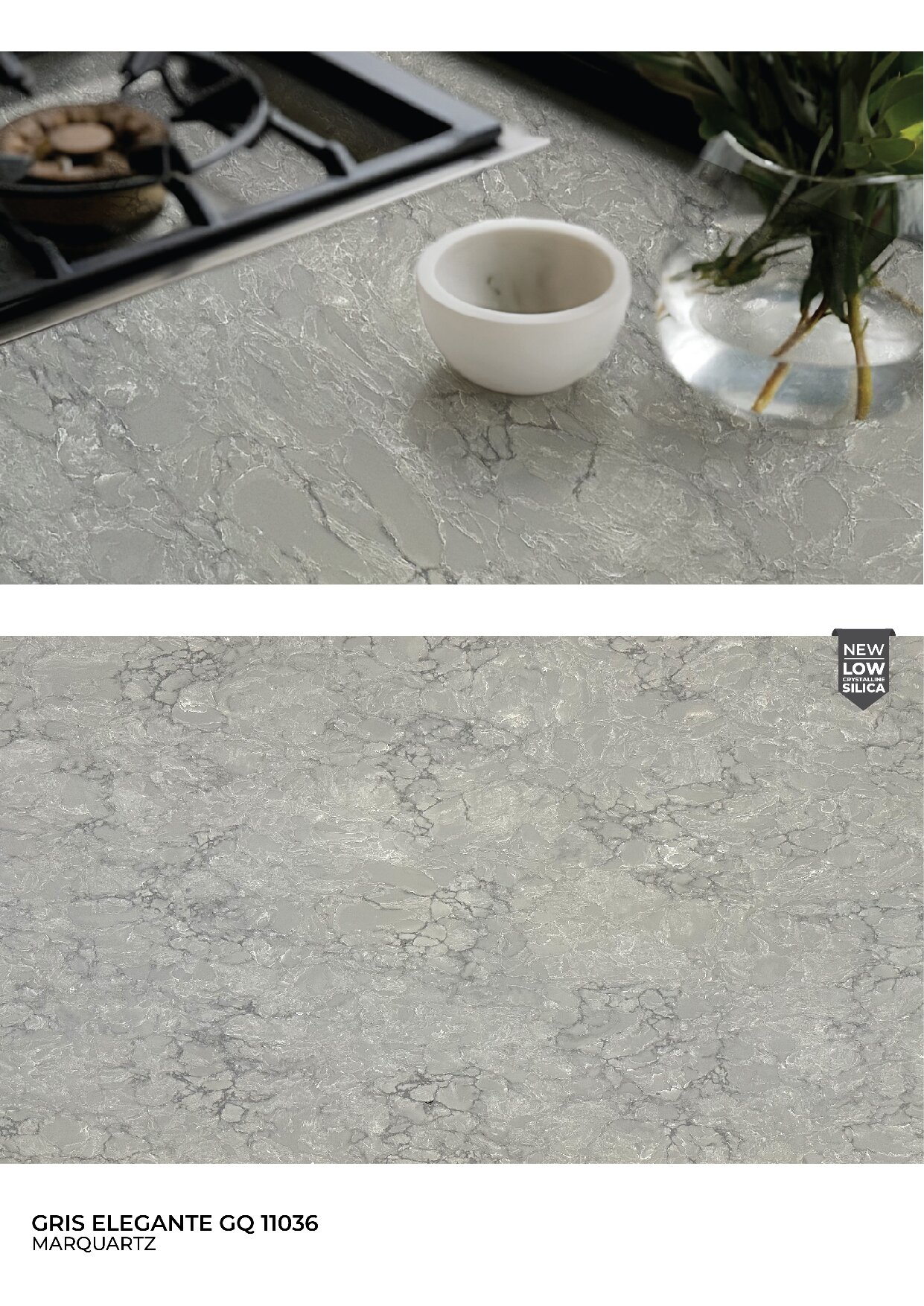
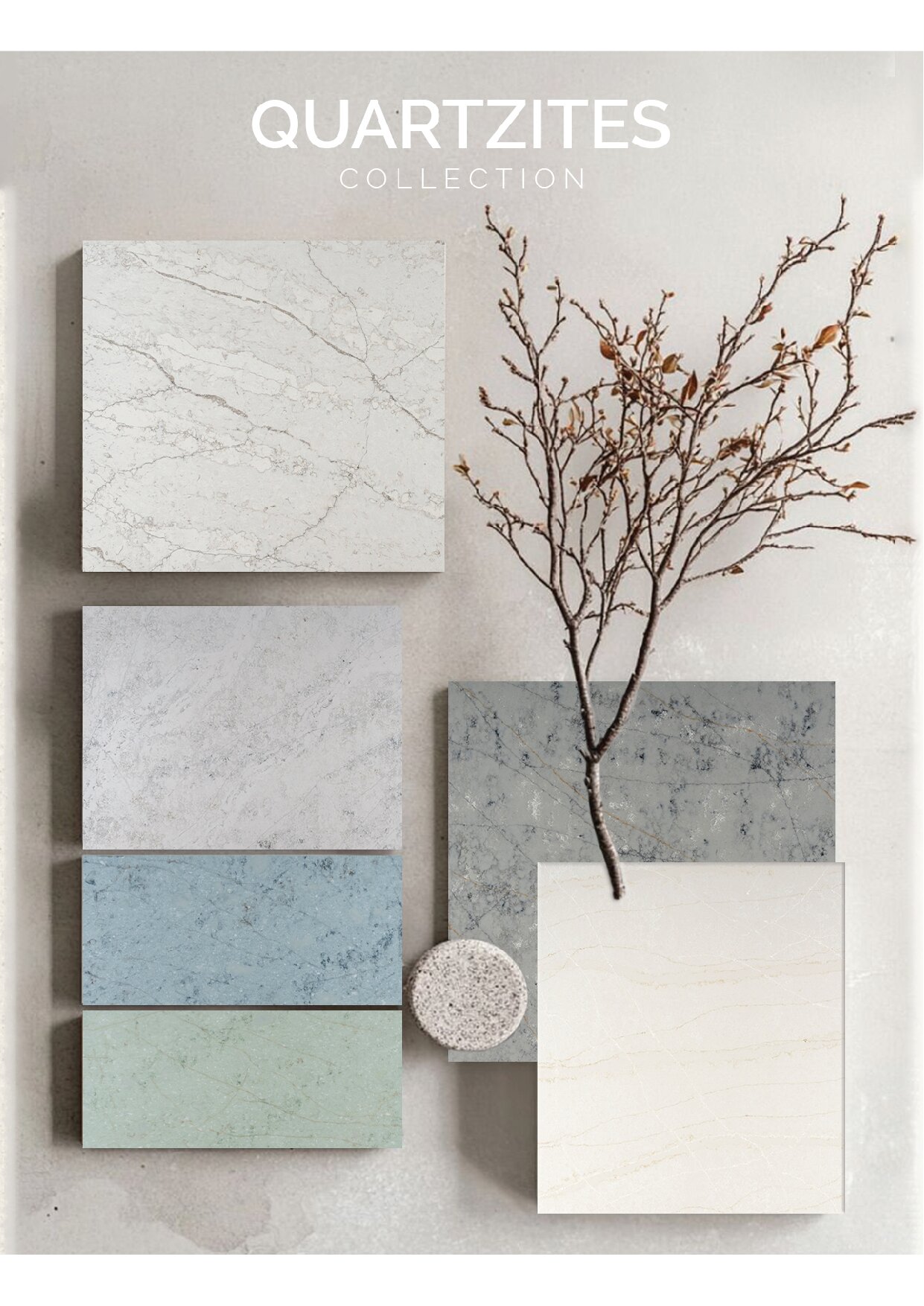
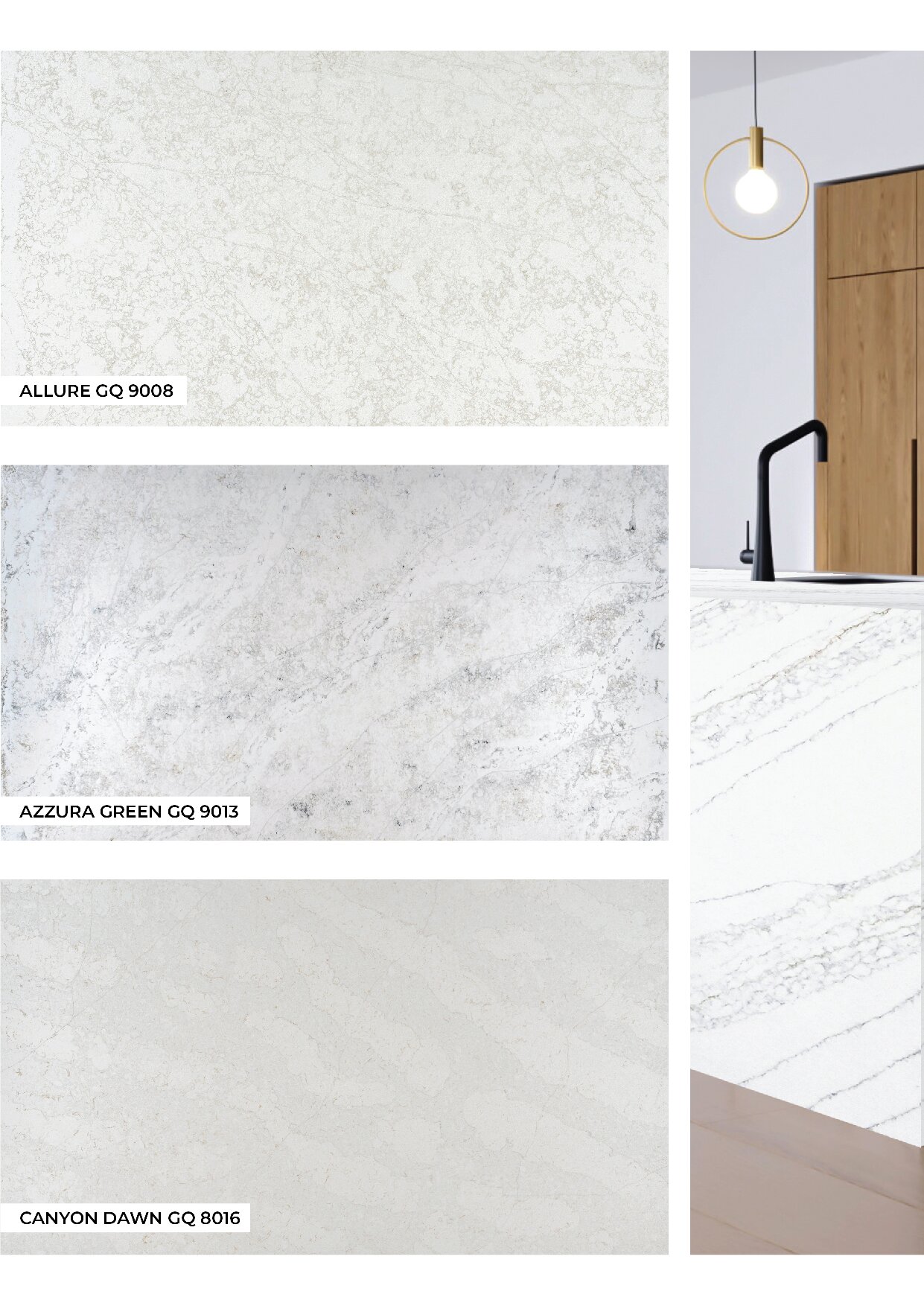
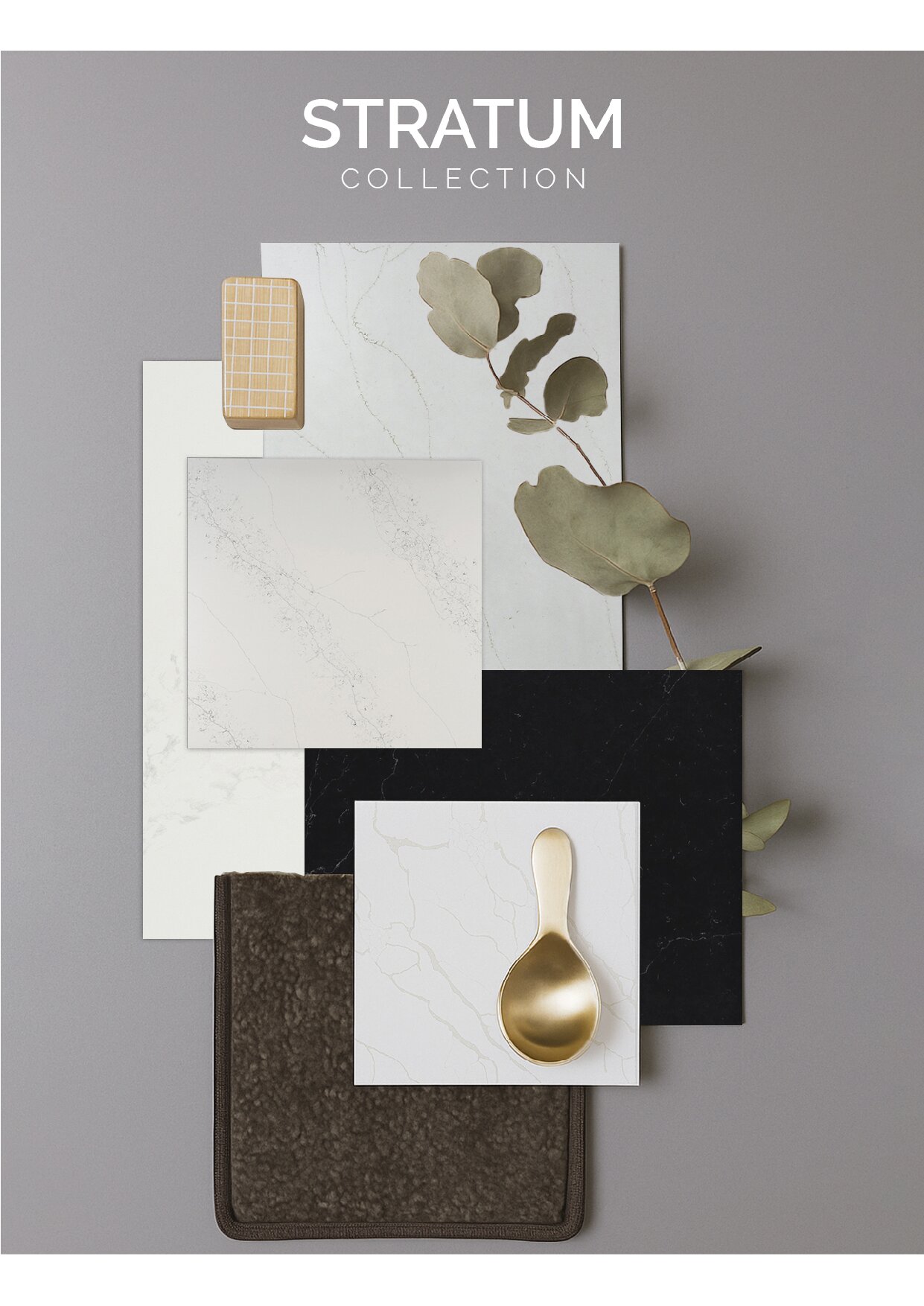
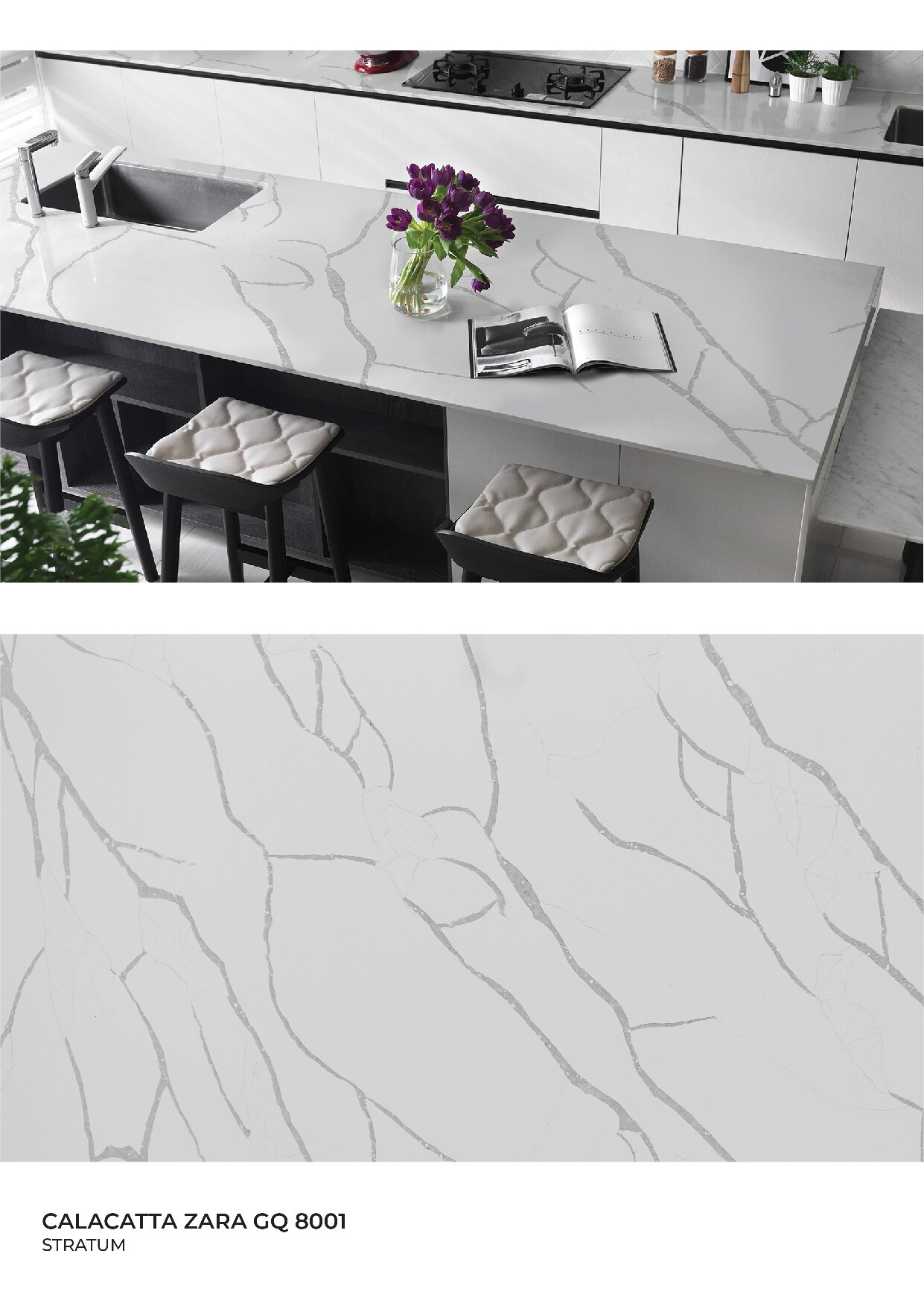
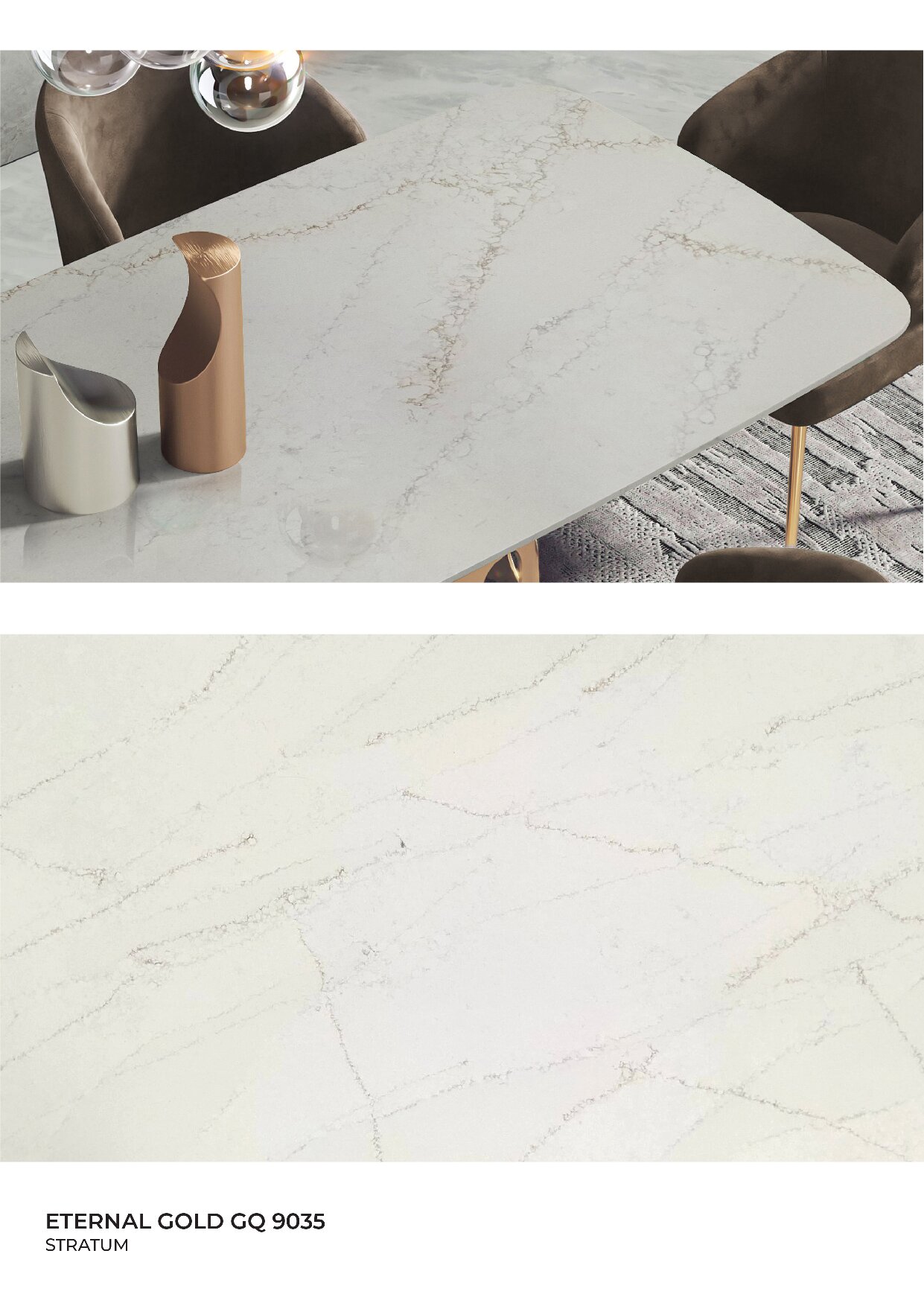
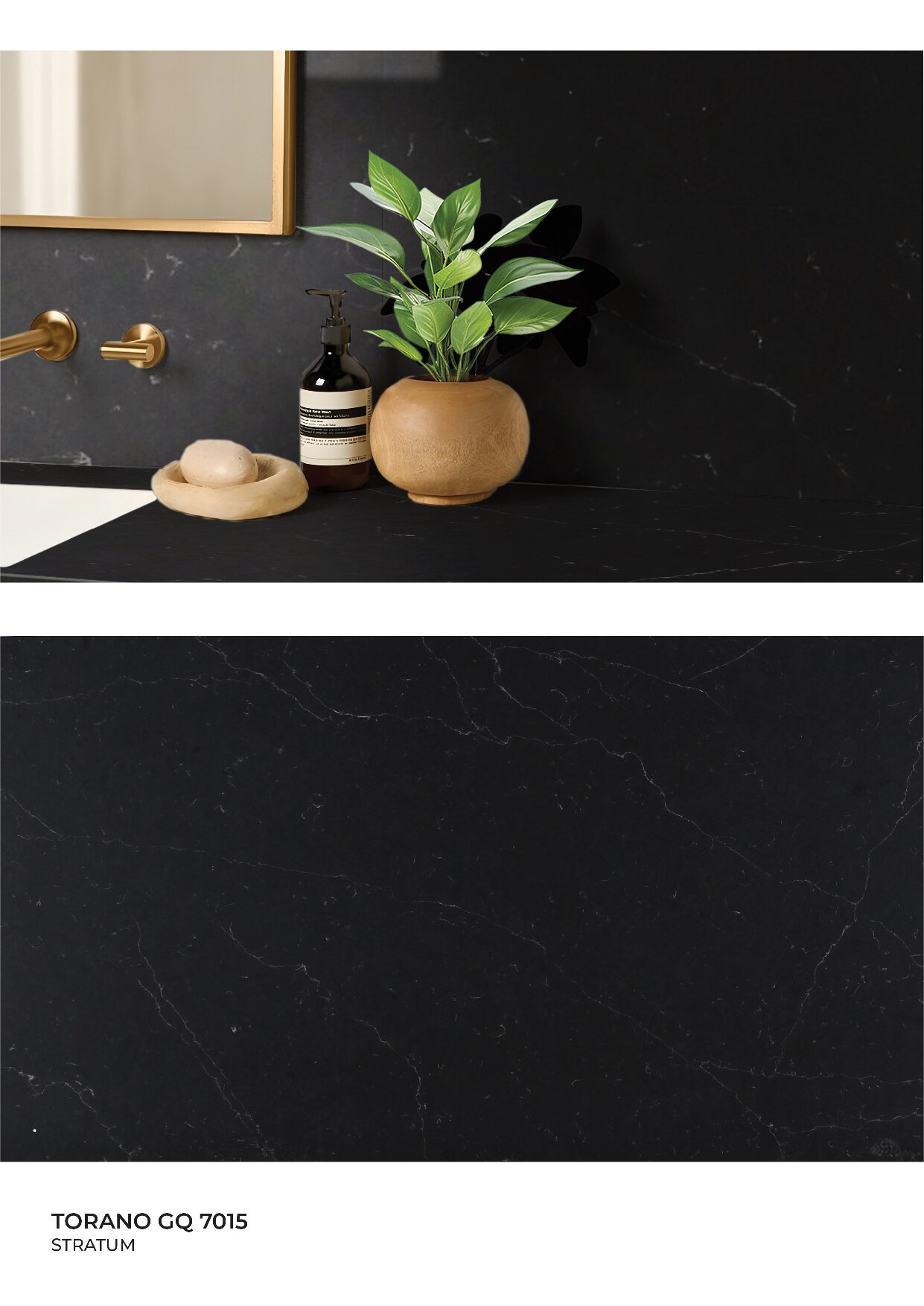
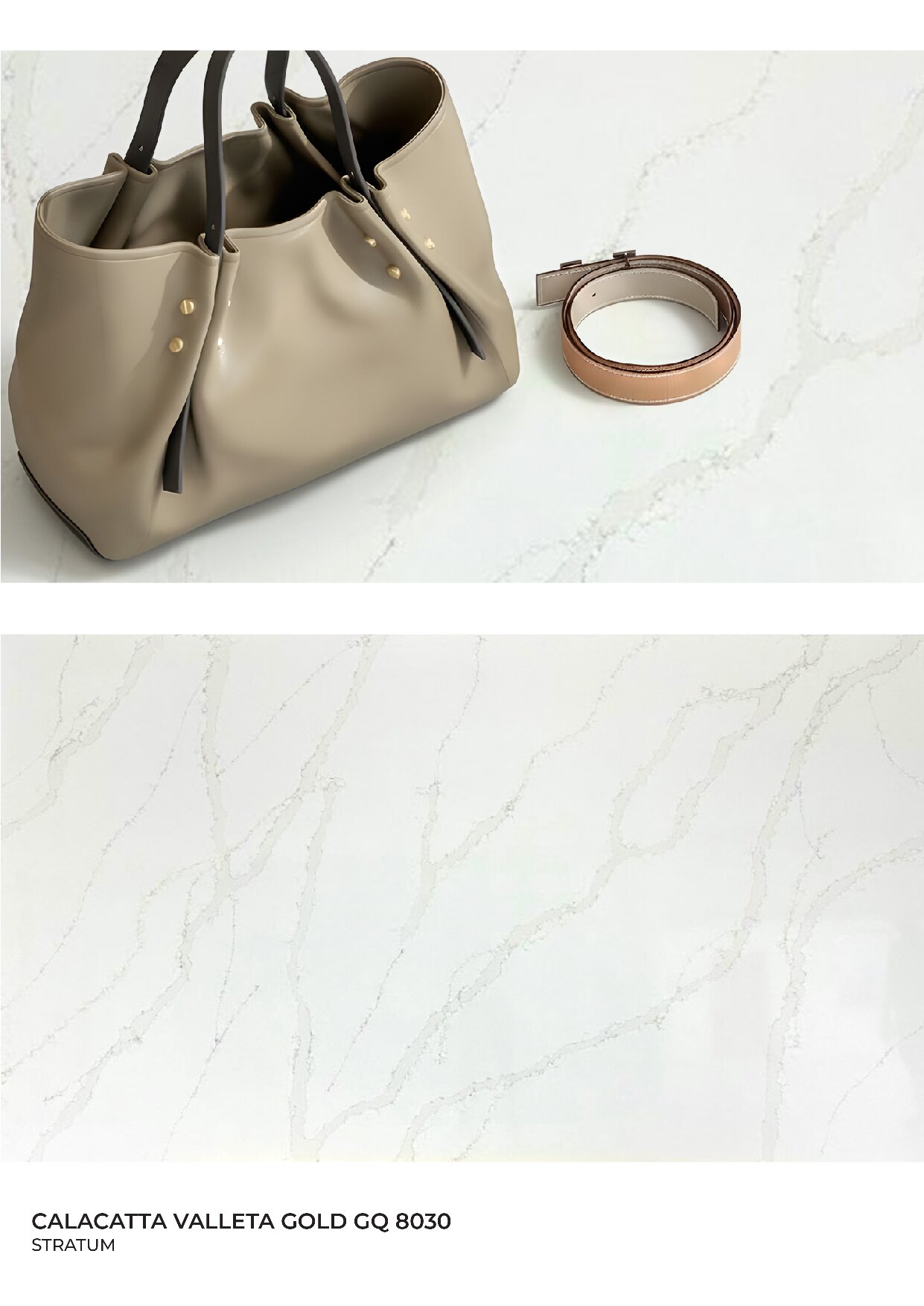
Global Surfaces
Summer Internship - Chemically Engineered Quartz
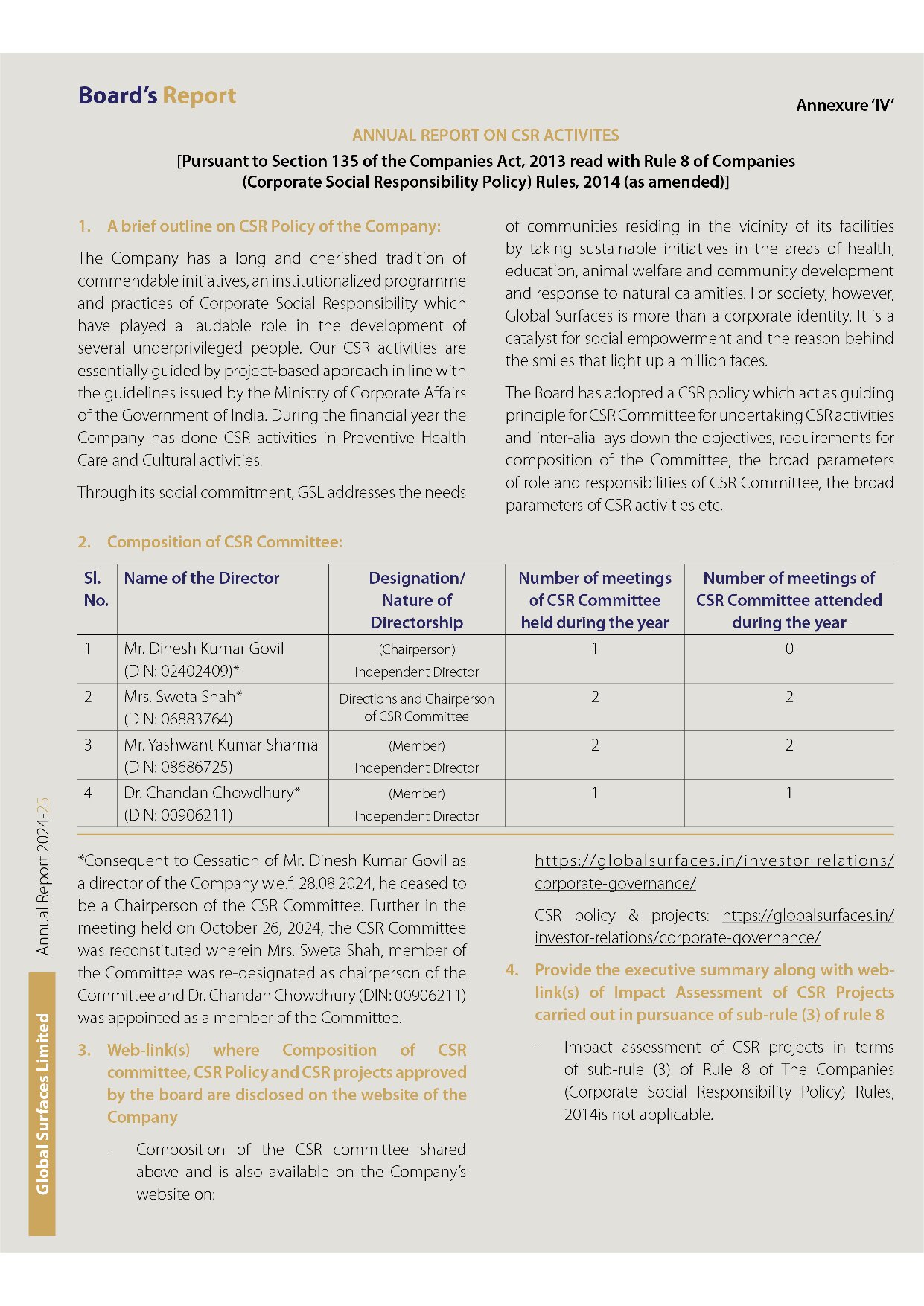
Timeline
12 weeks
Tools
Sketching
Market Research
Prototyping
Material Exploration
AutoCad
CNC machining
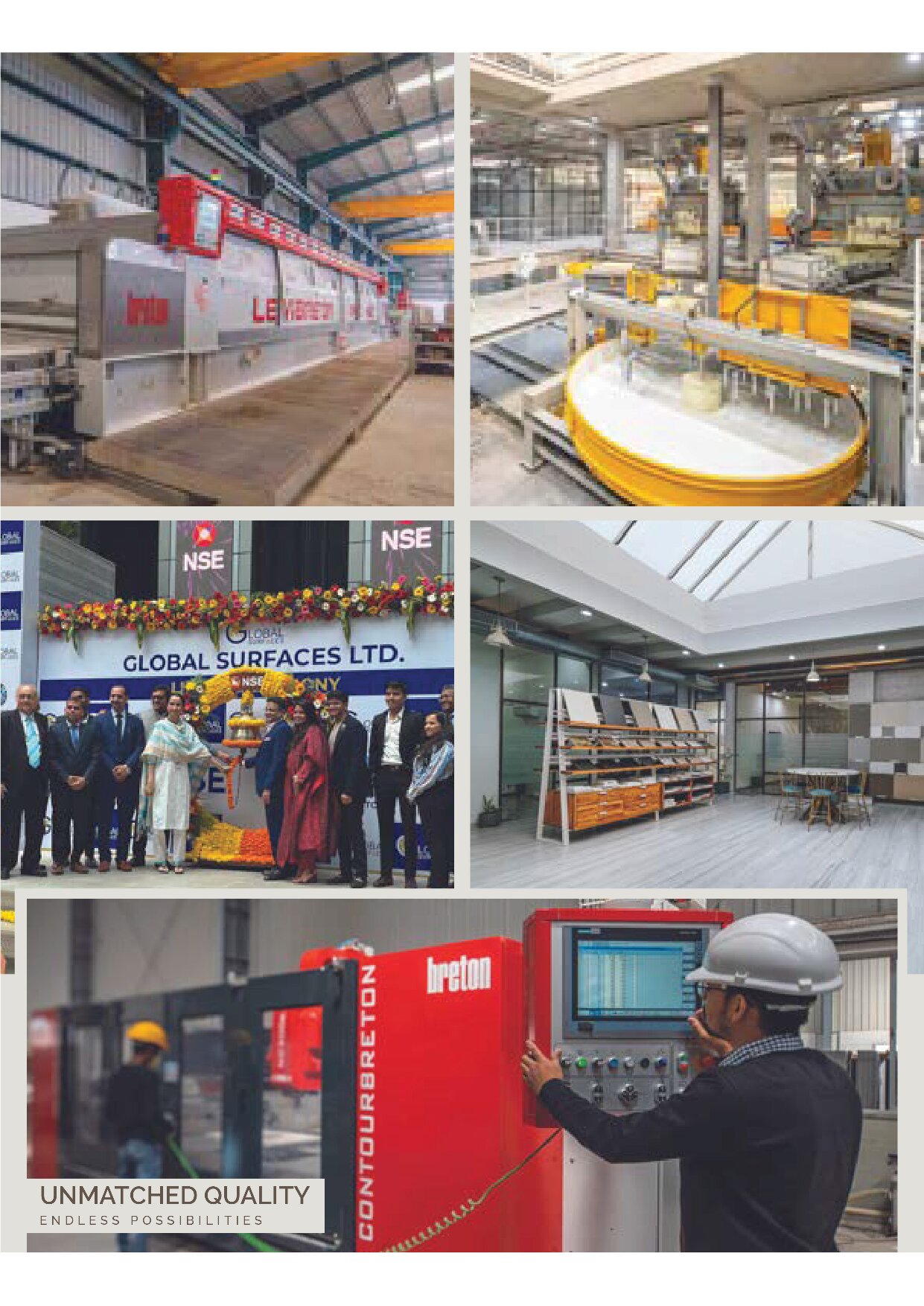
Manufacturing
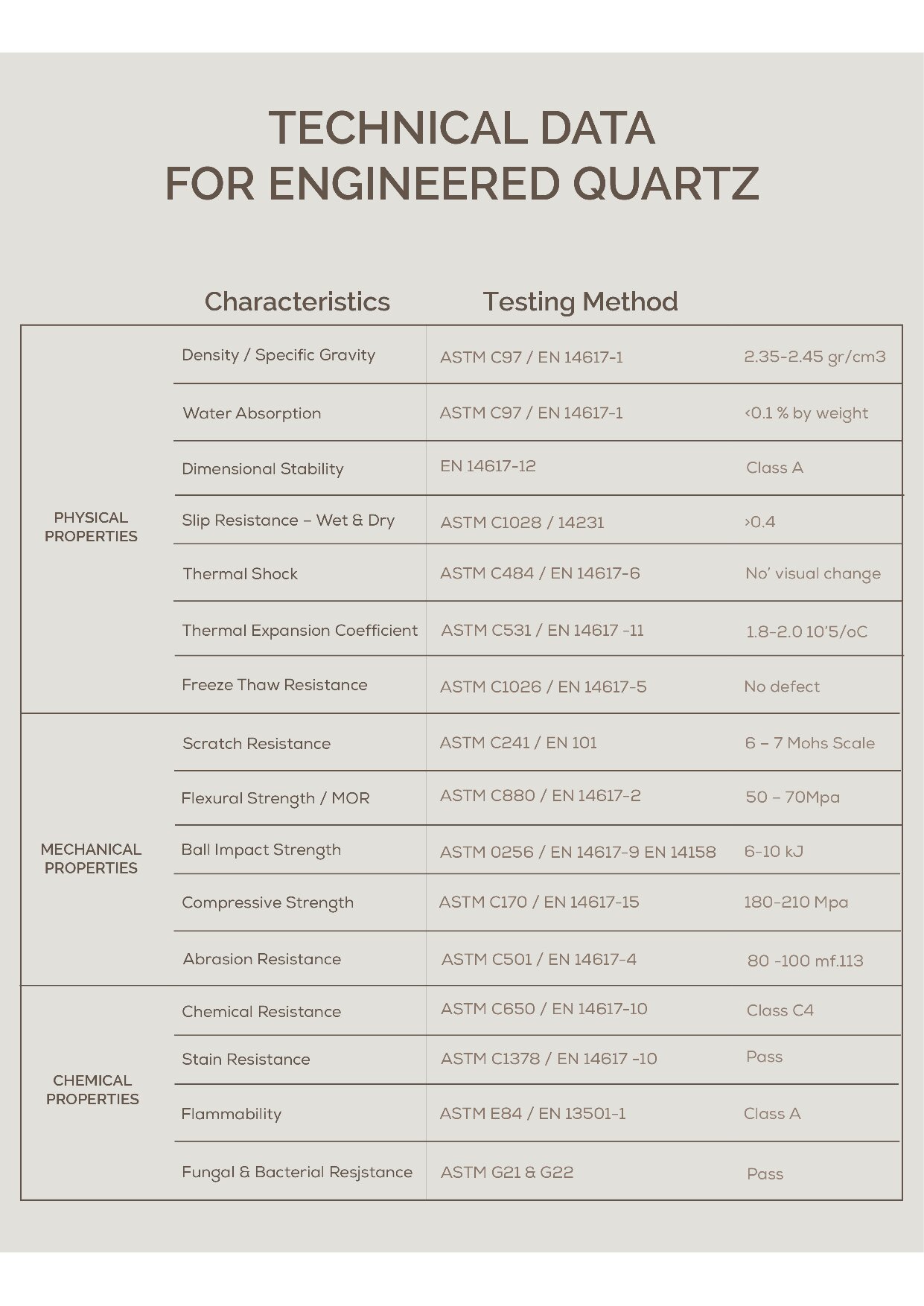
I gained extensive knowledge about the manufacturing process of engineered quartz. Serving as a material design intern, I collaborated closely with a team of engineers, designers, and manufacturers to develop chemically engineered quartz. My role was multifaceted, involving material research to understand the properties and applications of quartz, utilizing computer-aided design (CAD) to model our products, and operating CNC machinery for precise fabrication. Furthermore, I engaged in hands-on experimentation within their laboratory to produce miniature samples, which was crucial for testing and quality assurance. This comprehensive experience provided me with a deep understanding of the engineered quartz production process, from conceptual design to the actual manufacturing.
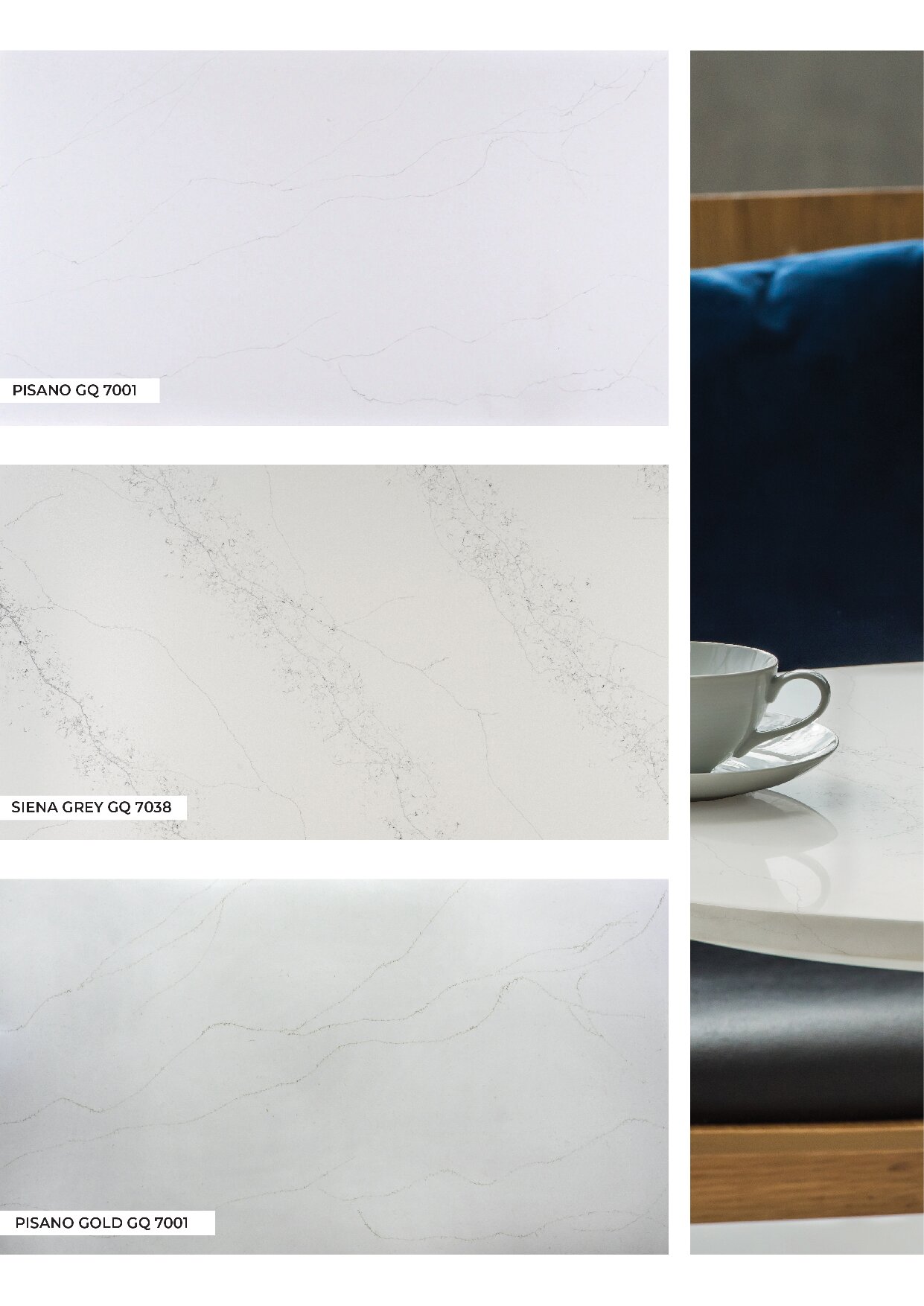
Engineered Quartz Lab Experiments


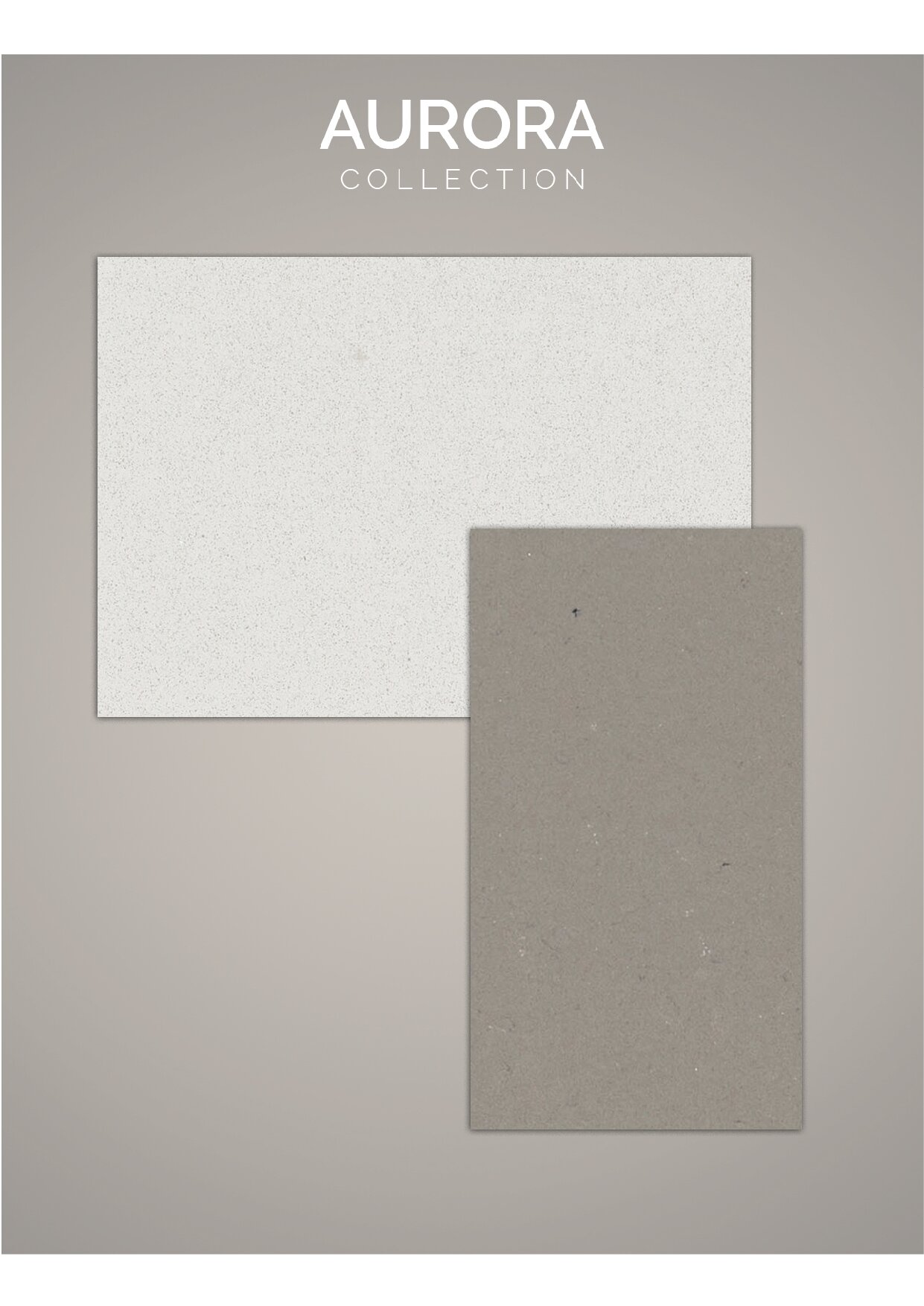
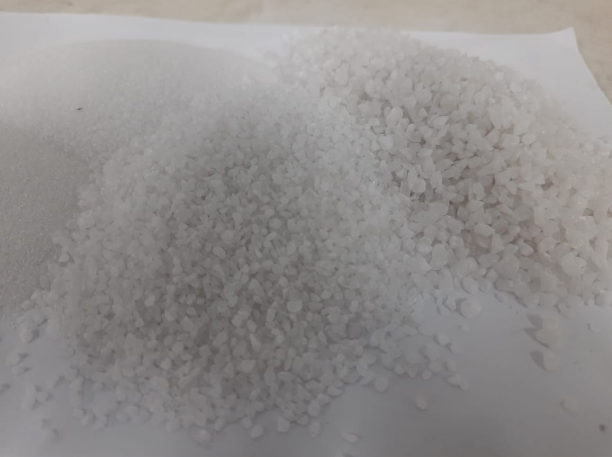
Mixing resin with pigments, quartz grit, quartz sand, powder, curing agents, and other chemicals to form miniature samples of slabs that mimic the appearance of natural stone or other desired textures and colors. This method is invaluable for visualizing the final product without the need to allocate significant resources or invest in full-scale manufacturing. By mixing raw materials in a laboratory setting and precisely measuring quantities, it is possible to determine the exact amount of pigments and materials required for the manufacturing process.
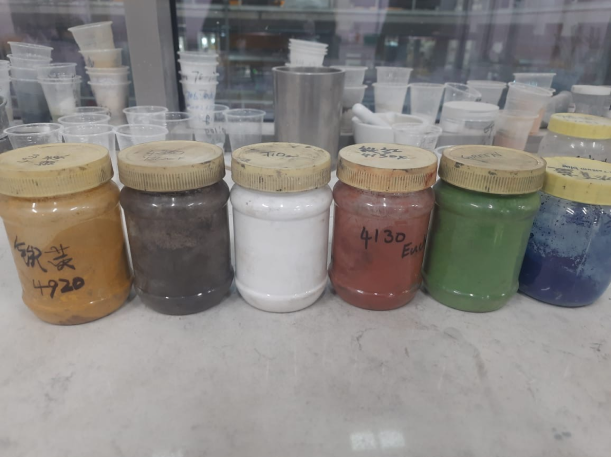


Mold and Pressure
After mixing the resin, pigments, quartz materials, and chemicals, the blend is spread into a 1 by 1 foot mold. Next, pressure is applied to ensure that the compounds tightly bond together. This step forms a solid, cohesive miniature slab that serves as a prototype for visual and quality assessments before full-scale production.

Applying pressure on a cured slab to test its strength.
CNC Machining and Compression
A CNC machine is employed to intricately draw and remove material from the base material, crafting grains and patterns that resemble natural stone or specific designs.
Cleaning the edges and Polishing
Squaring the edge and cutting to market requirements.
Polishing the Surface to achieve a smooth, flat, and shiny surface.
Putting the lab sample and the manufactured product side by side to compare them. .

Learning how to operate machines from Professionals
Observed professionals operate different machines to gain an understanding of the manufacturing process.